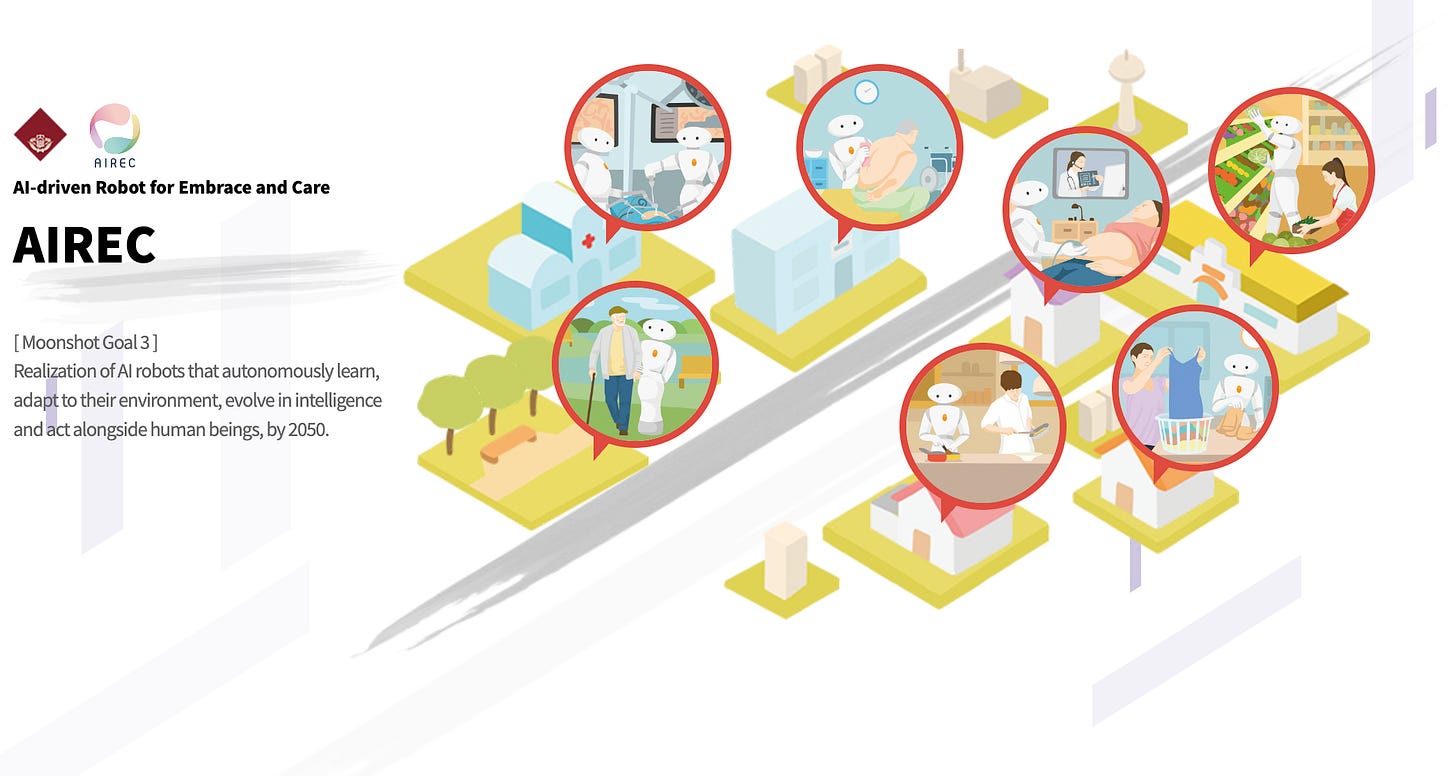
A National Challenge
Japan is facing a major problem: its population is getting older, and there are fewer young people to enter the workforce. By 2048, the population is expected to fall below 100 million. This has led to a serious shortage of workers, especially in caring for the elderly.
Turning to Technology
To solve this, Japan is investing heavily in technology like Artificial Intelligence (AI) and robotics. This includes everything from advanced humanoid robots like AIREC, which can help with difficult nursing tasks, to simpler gadgets like sleep sensors that monitor patients.
Society 5.0: A High-Tech Vision
This push is part of a national plan called "Society 5.0," which aims to build a "super-smart society" where technology solves everyday problems. As Japan develops these new technologies, it also faces important ethical questions about the role of machines in providing human care. The goal is for robots to help, not replace, human caregivers.
The Deepening Crisis: Fewer Workers, More Seniors
A Rapidly Aging Society
Japan is one of the fastest-aging countries in the world. In 2024, there were over 36 million people aged 65 or older. By 2065, nearly 40% of the population will be in this age group.
Falling Birth Rates
At the same time, birth rates have hit a record low, and this decline is happening much faster than predicted. This means a shrinking generation of young people is left to support a rapidly growing elderly population, putting immense pressure on social security and healthcare.
Severe Labor Shortage in Elder Care
This has created a severe worker shortage in the healthcare industry. For every person looking for a job in elder care, there are more than four job openings. The government estimated Japan will be short 370,000 caregivers by 2025. This shortage harms the quality of care and also hurts Japan's overall economy.
The Limits of Foreign Labor
Japan has started to accept more foreign workers, reaching a record 2.3 million in 2024. However, they still make up less than 3% of the aged-care workforce and only about 2% of the total labor force, which is much lower than in other developed countries. While policies are changing to welcome more workers, foreign labor alone cannot fill the massive gap.
Robots to the Rescue: A Technological Answer
The AIREC Project: A Human-Like Helper
A key project is AIREC, a 5-foot-7-inch tall humanoid robot being developed at Waseda University. It's designed to handle physically demanding tasks like lifting patients, helping them sit up, or even making simple meals. It uses advanced AI, pressure-sensitive fingers, and emotion recognition to interact safely and personally with people. AIREC is still a prototype and is expected to cost around $67,000 when it becomes available around 2030.
More Than Just Humanoids
Japan’s strategy isn't limited to complex robots like AIREC. A wide range of other technologies is also being used:
Monitoring Systems: Sensors placed under mattresses track sleep patterns, so staff don't have to do as many nighttime rounds.
Mobility Aids: Robotic devices help seniors walk, stand, and move between their bed and a wheelchair.
Companionship Robots: Small, friendly robots like the therapeutic seal PARO can reduce loneliness and lead to simple exercises.
Logistics Robots: In hospitals, robots like Moxi deliver supplies and lab samples, freeing up nurses to spend more time with patients.
This mix of different technologies, from simple sensors to advanced robots, shows a practical approach to solving the many challenges of elderly care.
A Foundation of Hardware Mastery
What gives Japan a unique edge is its long history as a world leader in industrial robots and precision manufacturing. While other countries focus on AI software, Japan excels at creating high-quality, reliable robot bodies needed to perform complex tasks in the real world. This expertise is crucial for building the next generation of carebots.
A Culture of Acceptance
Another special aspect is Japan's culture, which is often more accepting of robots. Unlike in many Western cultures, where robots are sometimes seen as a threat, in Japan they are often viewed as helpful partners. This makes it easier to introduce robots into sensitive roles, like caring for people. This has led to the creation of unique robots focused on social connection, such as the therapeutic seal PARO.
More Than Just Humanoids
Japan’s strategy isn't limited to complex robots. A wide range of other technologies is also being used:
Monitoring Systems: Sensors under mattresses track sleep patterns.
Mobility Aids: Robotic devices help seniors walk and move around.
Companionship Robots: Small, friendly robots reduce loneliness.
Logistics Robots: Robots in hospitals deliver supplies, freeing up nurses.
A National Plan for a Robotic Future
Society 5.0: A Human-Centered Vision
Japan's push for AI in healthcare is backed by its "Society 5.0" national vision. The government has launched plans to encourage robot adoption and has invested heavily, including a plan to spend $100 billion on AI-powered hospitals. This strong government support, combined with flexible regulations, aims to make Japan a world leader in robotics.
Learning from Defense Technology
Japan is also investing billions in AI and robotics for its defense sector. This research into advanced navigation, secure communication, and safe autonomous systems could lead to new technologies that can also be used in civilian healthcare, speeding up the development of care robots.
Challenges on the Path Forward
Obstacles to Adoption Despite the push for technology, there are major hurdles:
Cost: Advanced robots are expensive, making them hard for many care facilities to afford.
Digital Divide: Many elderly Japanese citizens are not comfortable with digital technology, which makes it difficult to introduce new high-tech solutions.
Social Acceptance: Many people may still prefer a human caregiver over a robot.
Reliability: The technology needs to be incredibly safe and reliable before it can be widely used for direct physical care.
Ethical Questions Using robots in caregiving also raises important ethical concerns:
Reduced Human Contact: Relying too much on robots could lead to loneliness and social isolation for the elderly.
Privacy: Robots with cameras and sensors collect a lot of sensitive data that must be protected.
Dignity: Some robot designs might feel demeaning or childish to elderly users.
Accountability: It's unclear who is responsible if a robot makes a mistake and causes harm.
The Future: Humans and Robots Working Together
The goal in Japan is not to replace human caregivers but to support them. The best path forward is a collaborative model where robots handle difficult or repetitive tasks, freeing up humans to provide the empathy, compassion, and complex communication that machines cannot.
To achieve this, Japan must continue to invest in a wide range of technologies, from simple aids to advanced robots. It is vital that elderly users and their caregivers are involved in the design process to ensure the technology is practical, user-friendly, and respectful.
As one of the first nations to face such an extreme aging crisis, the lessons Japan learns in balancing technology and humanity will provide a valuable model for the rest of the world.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Japan is at a turning point, using AI and robotics not to replace human touch, but to support it. By finding the right balance between technological innovation and compassionate care, Japan aims to solve its critical caregiver shortage. The path it forges today will not only shape its own future but may also light the way for other aging societies across the globe.
View the full deep dive article here:
https://helloworldjapan.com/robotics-in-care-how-japan-is-using-ai-to-solve-its-elderly-care-crisis/